top of page
POST-TREATMENT
CONTACT BASIN

The contact basin is a critical component used primarily in the treatment of water through chemical coagulation and floucculation processes. the contact basin serves as a mixing and reaction tank where wastewater is treated with coagulants or additional chemicals to facilitate the removal of suspended solids, organic matter, and other contaminants. The design of the basin allows for adequate retention time, ensuring that the influent water is mixed thoroughly with the added coagulants.
© ICR AMBIENTAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
CHARACTERISTICS & ADVANTAGES

Effluent Quality Improvement
Reduces pathogens, algae, and nuisance organisms, improving the overall quality of the discharge water.

Effective Pathogene Inactivation
Provides sufficient contact time for desinfectants to kill or inactivate bacteria, viruses, and protozoa, ensuring safe effluent discharge.
FILTERS
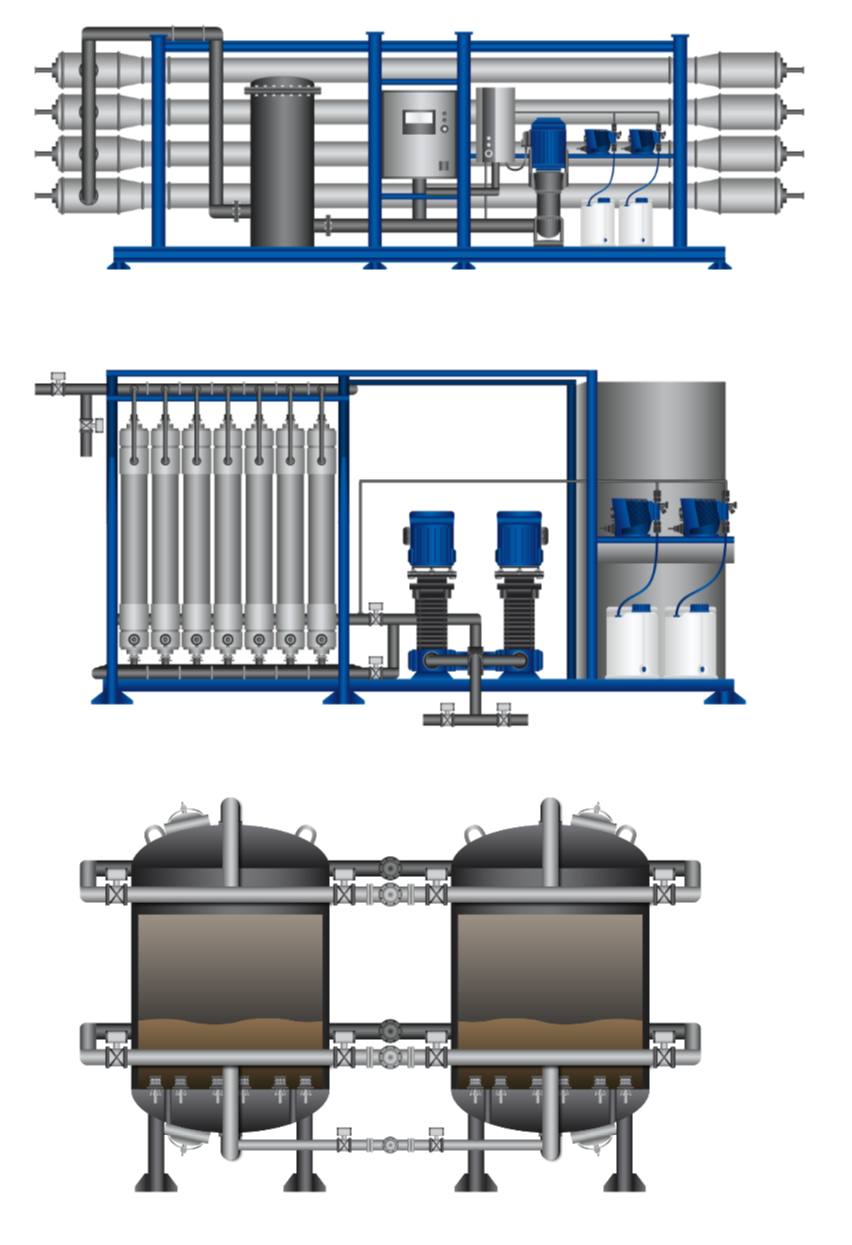
REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) FILTERS
A Reverse Osmosis (RO) filter is a membrane-based treatment process that uses semi-permeable membranes and high pressure to remove dissolved salts, organic compounds, microorganisms, and other contaminants from water. A Reverse Osmosis filter is usually applied after conventional and secondary treatment have already removed most solids and organic matter.
During the process, the treated wastewater is pressurized and forced across RO membranes. Pure water, known as permeate, passes through the membrane, while the remaining cancentrated stream, known as brine or reject, carries away dissolved impurities.
The main purpose of RO filters is to produce very high-quality effluent that can be reused for industrial processes, irrigation, boiler feed water, or, in advanced systems, even for potable reuse. The key advantage of RO is its ability to remove up to 99 percent of dissolved salts, heavy metals, pathogens, and other substances that are not removed by conventional treatment, making it one of the most effective polishing steps for water reuse.
ULTRAFILTRATION (UF)
Ultrafiltration is a membrane-based filtration process that removes very fine suspended solids, colloids, bacteria, and some viruses from wastewater. In a WWTP, the process involves pumping wastewater through UF membrane modules (hollow fiber, flat sheet, or spiral wound) under moderate pressure. The membranes act as a physical barrier, allowing water and low-molecular-weight solutes to pass through while retaining larger particles and micro-organisms. Periodic backwashing and chemical cleaning prevent fouling and maintain efficiency.
MULTIMEDIA FILTERS
A Multimedia Filter (MMF) is a pressure filter that relies on several layers of media to physically remove suspended solids and turbidity from water. Typically, the fitter contains anthracite at the top, sand in the middle, and garnet at the bottom, sometimes supported by gravel. As wastewater passes downward through the filter, larger particles are trapped in the coarse upper layers, while finer particles are captured in the lower, denser media. Over time, the filter accumulates solids and is cleaned through backwashing to restore performance.
The MMF is often used as a pretreatment step before sensitive downstream processes such as reverse osmosis, ultraviolet disinfection, or advanced oxidation. Its main role is to protect equipment and improve the clarity of water by removing suspended solids and reducing turbidity. Compared to single-media filters, multimedia filters are more efficient because their graded media structure allows for better solids retention and longer filter runs.
© ICR AMBIENTAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
© ICR AMBIENTAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
© ICR AMBIENTAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
CHARACTERISTICS & ADVANTAGES

Multimedia Filter
MMF acts as a pre-treatment, removing larger particles and protecting sensitive equipment.


Provides a barrier against fine particles and pathogens, ensuring safe, clean water for reuse or RO feed.
Ultrafiltration
Reverse Osmosis Filter
RO provides high-purity water, removing dissolved contaminants and making treated water reusable.
DAF - DISSOLVED AIR FLOTATION UNIT
A Dissolved Air Flotation - DAF unit is an advanced water treatment technology used to separate suspended solids, oils, grease, and other pollutants from water. The process relies on the principles of flotation, where fine air bubbles are introduced into the water, causing contaminants to rise to the surface for removal. This method is highly effective in treating industrial and municipal wastewater, particularly in applications where high levels of grease, oils, and other lightweight particles are present.
The operation of a DAF unit begins with the injection of air into a pressurized water stream. Air is dissolved into the water under pressure, creating a supersaturated solution. This pressurized water is then introduced into the main treatment tank, where the pressure is released, allowing the dissolved air to come out of the solution in the form of microbubbles. These tiny bubbles are crucial to the flotation process, as they attach to suspended particles, fats, and oils in the wastewater. The attachment of bubbles reduces the density of these contaminants, causing them to rise to the surface of the water.
As the bubbles and attached particles reach the surface, they form a floating layer of sludge. This layer is continuously or periodically skimmed off using mechanical scrapers, removing the bulk of the contaminants from the water. The floating materials are collected (by gravity) in the sludge hopper of the DAF unit and pumped with progressive cavity pumps to the sludge handling.
The clarified water beneath the surface is then directed to subsequent biological treatment stage for further purification.
The DAF unit is a fully automated "stand alone" unit equipped with feed system, internal recycle, micro bubble saturation system, sludge scraper and bottom hopper purge system.

© ICR AMBIENTAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
CHARACTERISTICS & ADVANTAGES

Excellent Removal of Light, Non-Settleable Solids

Compact and Fast Process
DAF is far superior to sedimentation for these contaminants.
Provides rapid clarification in a much smaller footprint compared to conventional primary clarifiers.
bottom of page
